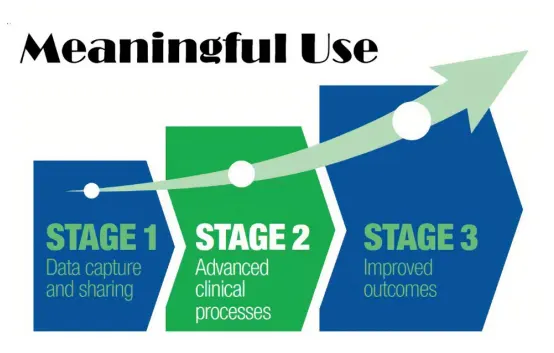
Meaningful use is a term used to describe the use of electronic health records (EHRs) in a way that can improve patient care and outcomes. In order to qualify for certain incentives and funding under the Meaningful Use program, healthcare organizations must meet specific criteria related to the use of EHRs. Clinical registry data abstraction is an important aspect of meeting these criteria.
One criterion for meaningful use is the ability to submit clinical quality measures (CQMs) to a registry or other qualified entity. Clinical registry data abstraction is the process of extracting relevant data from EHRs and other sources for the purpose of submitting CQMs. By accurately abstracting and submitting CQMs, healthcare organizations can demonstrate their meaningful use of EHRs and meet this criterion.
In addition to the submission of CQMs, clinical registry data abstraction can also be important for meeting other meaningful use criteria. For example, it can be used to track and report on progress towards meeting specific goals, such as reducing the rate of hospital readmissions or increasing the percentage of patients with a care plan.
Overall, clinical registry data abstraction is a crucial aspect of meeting meaningful use criteria and demonstrating the meaningful use of EHRs. By accurately abstracting and submitting relevant data, healthcare organizations can improve patient care and outcomes, as well as qualify for incentives and funding under the Meaningful Use program.